Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Key Insights and Hope
Understanding RA and Its Impact
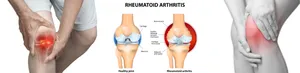
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the synovium, leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Over time, it can cause cartilage damage, joint deformities, and systemic complications involving organs like the lungs, heart, and eyes.
Recognizing Risks and Symptoms
RA arises from genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Key symptoms include:
- Persistent joint pain and stiffness, especially in the morning.
- Swelling and redness in joints, often symmetrically.
- Fatigue, weakness, and systemic signs like fever.
- Progressive joint deformity and functional loss if untreated.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Early diagnosis involves clinical evaluations, imaging (X-rays, MRIs), and blood tests (CRP, ESR, RF, anti-CCP). Treatments focus on reducing inflammation, slowing disease progression, and managing symptoms:
- Medications: DMARDs, biologics, NSAIDs, and corticosteroids.
- Therapies: Physical therapy, low-impact exercise, and dietary changes.
- Surgery: Reserved for advanced cases with severe joint damage.
Finding Support and Hope
Living well with RA is possible through early intervention and a comprehensive care plan. Working with a rheumatologist, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking emotional support are critical. Advances in treatments provide new hope for better management and improved quality of life.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for personalized guidance.